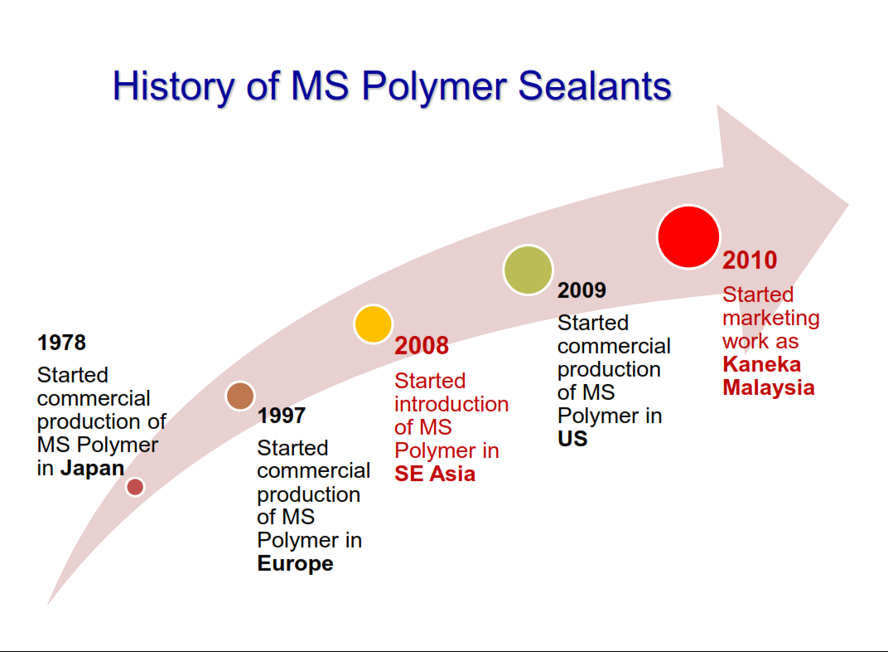
High performance sealant for precast concrete panels
High performance MS sealant for precast concrete panels

- Environmental friendliness (solvent-free and isocyanate-free)
- Low temperature gunnability: the viscosity of MS sealants is less dependent on temperature changes storage stability: shelf life is excellent although sealant must be protected from moisture
- Weather resistance and durability: MS sealant shows no cracking, splitting, discoloration or adhesion failure after ten years of testing in desert climate
- Stain resistance: MS sealants do not stain as some silicone sealants do because of low molecular weight silicon materials that bleed from the surface of sealed joints
- Paintability: MS sealants provide good paintability unlike silicone sealants adhesion



